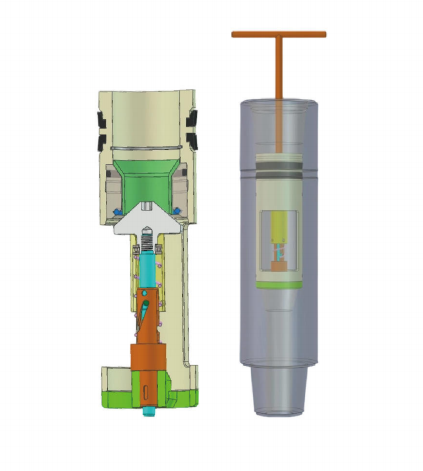
I. Structural Composition
1. Main Components:
- Knob and Actuation Mechanism: Controls valve opening/closing via a specialized wrench.
- Ball Valve Assembly: Includes a floating ball and movable valve seat.
- Fixed Valve Seat: Forms the primary sealing surface with the movable seat.
- Enlarged Chamber: A specialized cavity located in the lower valve body.
- Shear Pin Mechanism: Fixed pins designed with a 5MPa shear strength.
- Spring Reset System: Restores initial state after pressure balancing.
2. Core Functional Components:
- Dual Sealing System: Primary seal (ball-to-seat) and secondary seal (enlarged chamber).
- Pressure-Triggered Mechanism: Overload protection via shear pins and springs.
- Check Valve Configuration: Forms a unidirectional flow path through ball and seat repositioning.
II. Working Principle
(A) Normal Closure Mode
1. Manual Operation:
- When overflow or blowout is detected, operators rotate the knob 90° clockwise using a wrench.
- The ball aligns fully with the valve seat, and the positioning surface contacts the fixed seat.
- A metal-to-metal hard seal is formed, completely blocking the mud flow path.
2. Pressure Isolation:
- Withstands bidirectional pressure in the closed state.
- Prevents upward transmission of formation pressure (up to 70MPa).
- Protects surface equipment (e.g., rotary hose, standpipe) from overpressure damage.
(B) Check Valve Mode (Overload Protection)
1. Activation Conditions:
- Forward pressure differential ≥5MPa (upper ball pressure minus lower pressure).
- Scenarios include:
- Post-closure jamming preventing manual reopening.
- Need for temporary circulation channels.
- Special well depth requirements for unidirectional flow.
2. Automatic Transition Process:
- Shear Pin Failure: Precision-engineered pins fracture at 5MPa differential.
- Component Downward Shift: The floating ball and movable seat compress the spring, moving downward 8–10mm.
- Seal Reconfiguration: The sealing section enters the enlarged chamber, creating an annular gap.
- Unidirectional Flow Path: Mud flows downward (fixed seat → movable seat) but reverse flow is blocked.
3. Functional Features:
- Maintains pressure balance while enabling controlled pressure relief.
- Prevents "pressure lock" post-closure.
- Provides a flow channel for subsequent well-killing operations.
This device employs a mechanical-hydraulic linkage design to ensure reliable pressure control under both routine and emergency conditions. As critical safety equipment for deep and ultra-deep wells, its innovative pressure-triggered mechanism reduces emergency response time by over 60% compared to traditional plug valves, significantly enhancing well control safety.