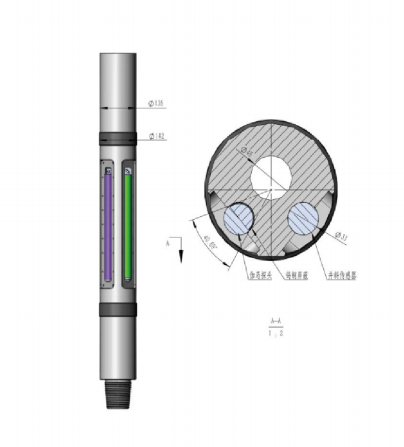
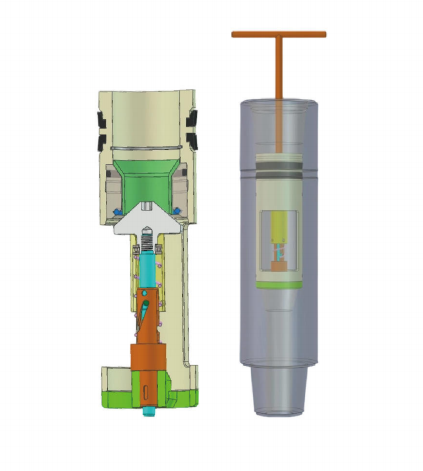
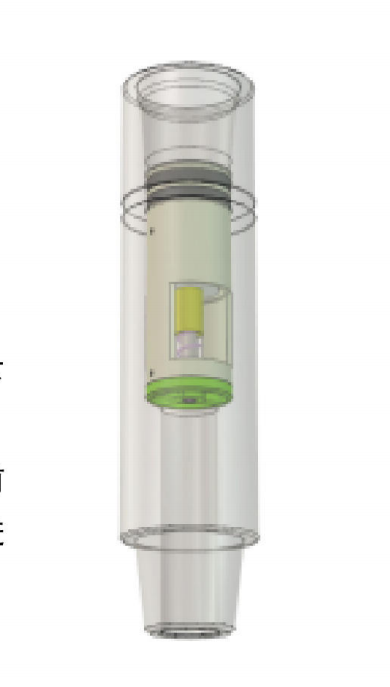
1. Preparation Phase
Geological Exploration:
Use seismic exploration and geological surveys to identify potential oil and gas reservoirs.
Collect geological data to assess the potential and risks of the reservoirs.
Site Selection:
Choose the drilling location based on geological data, considering factors such as terrain, environment, and infrastructure.
Obtain land use rights and necessary permits.
Equipment and Personnel Preparation:
Prepare drilling equipment, including drilling rigs, drill pipes, drill bits, mud systems, etc.
Assemble a professional drilling team, including drilling engineers, geologists, mud engineers, etc.
2. Pre-Drilling Preparations
Drilling Platform Construction:
Build the drilling platform, including the drilling derrick, mud pits, mud circulation system, etc.
Install and commission drilling equipment to ensure it is in good working order.
Mud System Preparation:
Prepare drilling fluid (mud) to ensure it meets the drilling requirements.
Set up the mud circulation system, including mud pumps, mud pits, mud purification equipment, etc.
3. Drilling Process
Surface Drilling:
Drill the surface layers, typically including the surface and shallow layers.
Install surface casing to stabilize the wellhead and prevent wellbore collapse.
Intermediate Drilling:
Continue drilling the intermediate layers, adjusting drilling parameters based on geological data.
Install intermediate casing to further stabilize the wellbore and prevent formation fluids from entering the wellbore.
Target Layer Drilling:
Drill the target layer, i.e., the potential oil and gas reservoir layer.
Use directional drilling techniques to ensure the drill bit accurately reaches the target location.
Install production casing in preparation for completion operations.
4. Completion Operations
Cementing:
Inject cement slurry into the annular space between the casing and the wellbore to ensure the seal between the casing and the wellbore.
Conduct pressure tests after cementing to ensure the integrity of the wellbore.
Perforation:
Use perforating guns to create holes in the production casing, allowing oil and gas to flow into the wellbore.
Perform acidizing or fracturing to enhance the permeability of the oil and gas.
Installation of Production Equipment:
Install production equipment such as the Christmas tree, tubing, valves, etc.
Conduct a trial production to test the oil and gas production and well performance.
5. Production and Monitoring
Oil and Gas Production:
Begin the formal production of oil and gas, transporting them to the surface through the Christmas tree and tubing.
Regularly monitor the production data of the well, including production, pressure, temperature, etc.
Well Maintenance and Management:
Regularly maintain the well, including wax removal, acidizing, fracturing, and other production enhancement measures.
Monitor the health of the well, promptly address downhole issues, and ensure stable production.
6. Post-Drilling Activities
Data Recording and Analysis:
Record all data from the drilling process, including geological data, drilling parameters, production data, etc.
Analyze the data to assess the drilling results and provide references for future drilling operations.
Environmental Protection:
Handle the waste generated during the drilling process, including drill cuttings and mud.
Take measures to reduce environmental impact and ensure compliance with environmental standards.