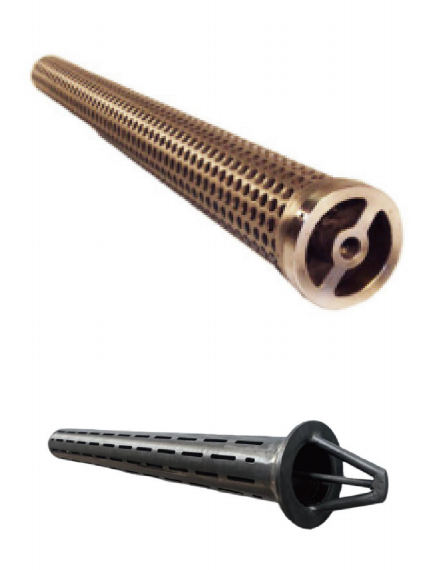
During drilling operations, a drill string float valve is installed in the drill pipe to:
1. Prevent annular drilling fluid from flowing back into the drill string when connecting pipes or tripping out, avoiding fluid spillage onto the drill floor.
2. Block formation fluids from entering the drill string, mitigating risks of kicks or blowouts.
Float valves are categorized by structure and function:
- By Structure: Flapper valves vs. Poppet valves.
- By Function: Blind valves vs. Vented valves.
I. Classification by Valve Core Structure
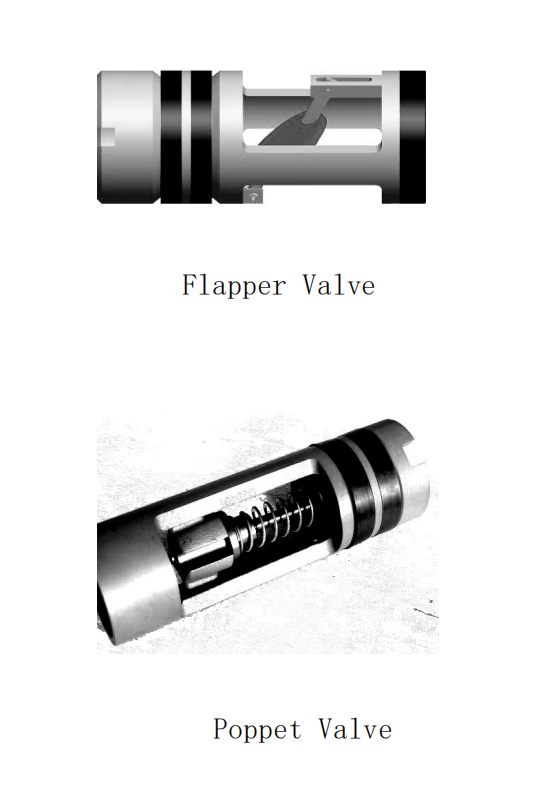
1. Flapper Float Valve
- Structure: Features a hinged metal/composite flapper (like a "swinging door").
- Working Principle:
- Forward Flow: Drilling fluid pressure opens the flapper.
- Reverse Flow: The flapper closes automatically via gravity/spring force.
- Advantages:
- Rapid closure (<1 sec), reliable sealing.
- Resistant to abrasive fluids (e.g., cuttings-laden mud).
- Limitation: Delayed response in high-viscosity fluids.
2. Poppet Float Valve
- Structure: Uses a conical/arrow-shaped piston with a guide rod and sealing seat.
- Working Principle:
- Forward Flow: Fluid lifts the piston to open the channel.
- Reverse Flow: The piston drops into the seat to seal the passage.
- Advantages:
- Large flow area, low pressure drop.
- Resists clogging by solids.
- Limitation: Sealing surface wear under high pressure.
II. Classification by Function
1. Blind Float Valve
- Function: Completely seals the drill string channel when closed.
- Use Case:
- High-risk well control (e.g., HPHT gas zones).
- Absolute backflow prevention during tripping.
2. Vented Float Valve
- Function: Contains a small vent hole (Ø3–6 mm) in the valve core.
- Key Advantages:
- Downhole pressure monitoring via surface gauges.
- Pressure balance to prevent water hammer.
- Use Case:
- Precision well control (e.g., narrow drilling windows).
- Operations requiring pressure data (cementing, testing).
III. Applications & Industry Trends
Critical Scenarios
- Pipe Connection:
- Stops annular fluid backflow during pump shutdowns.
- Kick Response:
- Blind valves: Isolate flow entirely for BOP activation.
- Vented valves: Monitor pressure changes while sealing.
Innovations
- Smart Valves: Integrated sensors for real-time downhole data.
- HT Materials: Silicon carbide seals (>200°C/392°F tolerance).
- Modular Kits: Interchangeable flapper/poppet cores.
Summary
Flapper and poppet float valves act as "gatekeepers" of the drill string:
- Flapper valves excel in rapid sealing with solids-laden fluids.
- Poppet valves offer efficient flow in high-pressure, large-volume scenarios.
Paired with blind/vented designs, they enable adaptable well control for diverse drilling operations.