Hydraulic Oscillator: Revolutionizing Weight-on-Bit Transfer in Directional Drilling
The Challenge of Extended-Reach Drilling
In long lateral and directional wells, drillers face:
-Poor weight-on-bit (WOB) transfer reducing ROP by 30-50%
-High friction factors causing stick-slip and torsional vibrations
-Tool face instability requiring constant correction cycles
-Increased stuck pipe risk in high-angle sections
Our hydraulic oscillator delivers:
✅ 50% friction reduction between BHA and wellbore
✅ 90% improved WOB transfer to the bit
✅ Tool face stability even in complex formations
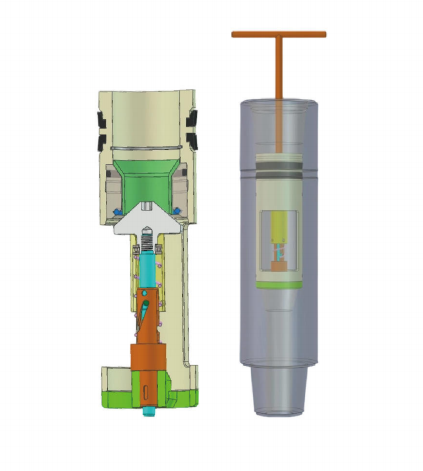
How It Works: Axial Vibration Technology
Three-Core Component System
Component | Function | Innovation |
Oscillation Section | Generates high-frequency axial vibrations | 15-25 Hz optimized frequency range |
Power Section | Converts hydraulic energy to mechanical motion | Positive displacement motor design |
Valve & Bearing System | Controls oscillation timing and amplitude | Precision machined for 500+ hours life |
→ Self-powered by drilling mud flow - no electrical components
→ Adjustable frequency based on flow rate
Operational Advantages
✅ Drilling Efficiency
35% higher ROP through improved WOB transfer
60% reduction in stick-slip vibrations
✅ Directional Control
Tool face stability within ±5° maintained
Fewer orientation cycles required
✅ Risk Reduction
70% lower stuck pipe risk
Prevents wellbore spiraling and micro-doglegs
✅ Equipment Protection
Reduces MWD/LWD tool failures by 45%
Extends motor and BHA life
Technical Specifications
Parameter | Specification |
OD Range | 6-3/4" to 9-7/8" (slimhole to conventional) |
Flow Rate Range | 300-850 GPM |
Operating Pressure | 300-500 psi differential |
Frequency Range | 15-25 Hz (adjustable via flow rate) |
Amplitude | ±0.5-1.5 inches |
Connections | API REG, IF, FH (all standard sizes) |
Temperature Rating | -20°C to 175°C |
Field Applications
Extended Reach Drilling: Enables longer laterals with improved weight transfer
Directional Wells: Maintains tool face control in complex formations
Unconventional Shale: Reduces friction in curve and lateral sections
Slimhole Operations: Prevents sticking in restricted diameters
Hard Formations: Reduces stick-slip and improves cutter engagement